本系列将一步步讲解和演示 TensorFlow 的使用, 本篇主要介绍如何跑起来一个开发 TensorFlow 的环境。
Installation
对于初学者来说从 Docker Container 启动 TensorFlow 学习环境是个不错(不费力)的选择。
use Docker
所使用的 Docker 容器镜像为 tensorflow TensorFlow Docker
在使用 Docker 之前可以添加一些 Docker 的国内镜像 Docker Hub 镜像, 使下载镜像速度加快。
如果直接运行如下命令,容器会建立一个 Jupyter notebook 服务来帮助你学习 python 语言
docker run --name=my-tensorflow -it -p 8888:8888 tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-py3-jupyter
还可以运行 bash 命令行工具,然后运行 python 命令行环境
$ docker run --name=my-tensorflow -it tensorflow/tensorflow bash
root@06a6c03e3e74:/notebooks# python
Python 2.7.12 (default, Dec 4 2017, 14:50:18)
[GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
On Windows (Optional)
TensorFlow supports Python 3.5.x and 3.6.x on Windows. Note that Python 3 comes with the pip3 package manager, which is the program you’ll use to install TensorFlow.
> python --version
Python 3.6.6
Install CPU-only version of TensorFlow
> pip3 install --upgrade tensorflow
To install the GPU version of TensorFlow
> pip3 install --upgrade tensorflow-gpu
First Graph
现在就来创建一个最简单的 TensorFlow 图,如下图所示
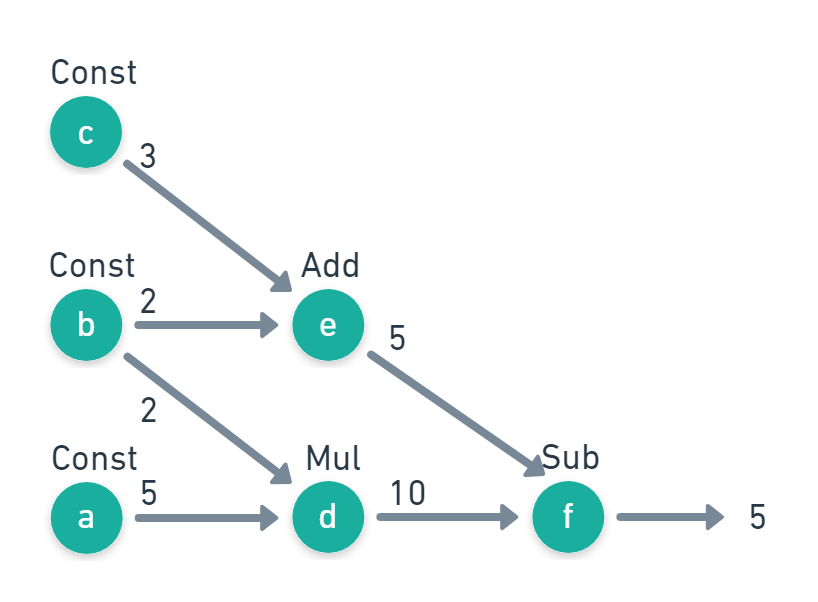
TensorFlow 代码如下
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
a = tf.constant(5)
b = tf.constant(2)
c = tf.constant(3)
d = tf.multiply(a,b)
e = tf.add(c,b)
f = tf.subtract(d,e)
print(f)
print("outs = {}".format(f))
# Outputs:
# tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
# outs = 5
如果你使用的环境没有 Matplotlib 可以通过下面命令安装
pip3 install --upgrade matplotlib
Tensor
张量(英语:Tensor)是一个可用来表示在一些矢量、标量和其他张量之间的线性关系的多线性函数, 这些线性关系的基本例子有内积、外积、线性映射以及笛卡儿积.
These are our Tensors
print(tf.constant(1).shape)
print(tf.constant([1,2]).shape)
print(tf.constant([[1],[2]]).shape)
print(tf.constant([[1,2]]).shape)
print(tf.constant(np.array([
[[1,2],
[3,4]],
[[5,6],
[7,8]]])).get_shape())
# Outputs:
# ()
# (2,)
# (2, 1)
# (1, 2)
# (2, 2, 2)
Regression model
本章节我们用 TensorFlow Graph 构建一个线性回归模型 (Linear Regression)。假设我们有这样一个数学模型,其实他是一个多元线性回归函数
\[f(x_i) = w^Tx_i + b\]此模型所对应的矩阵运算如下图
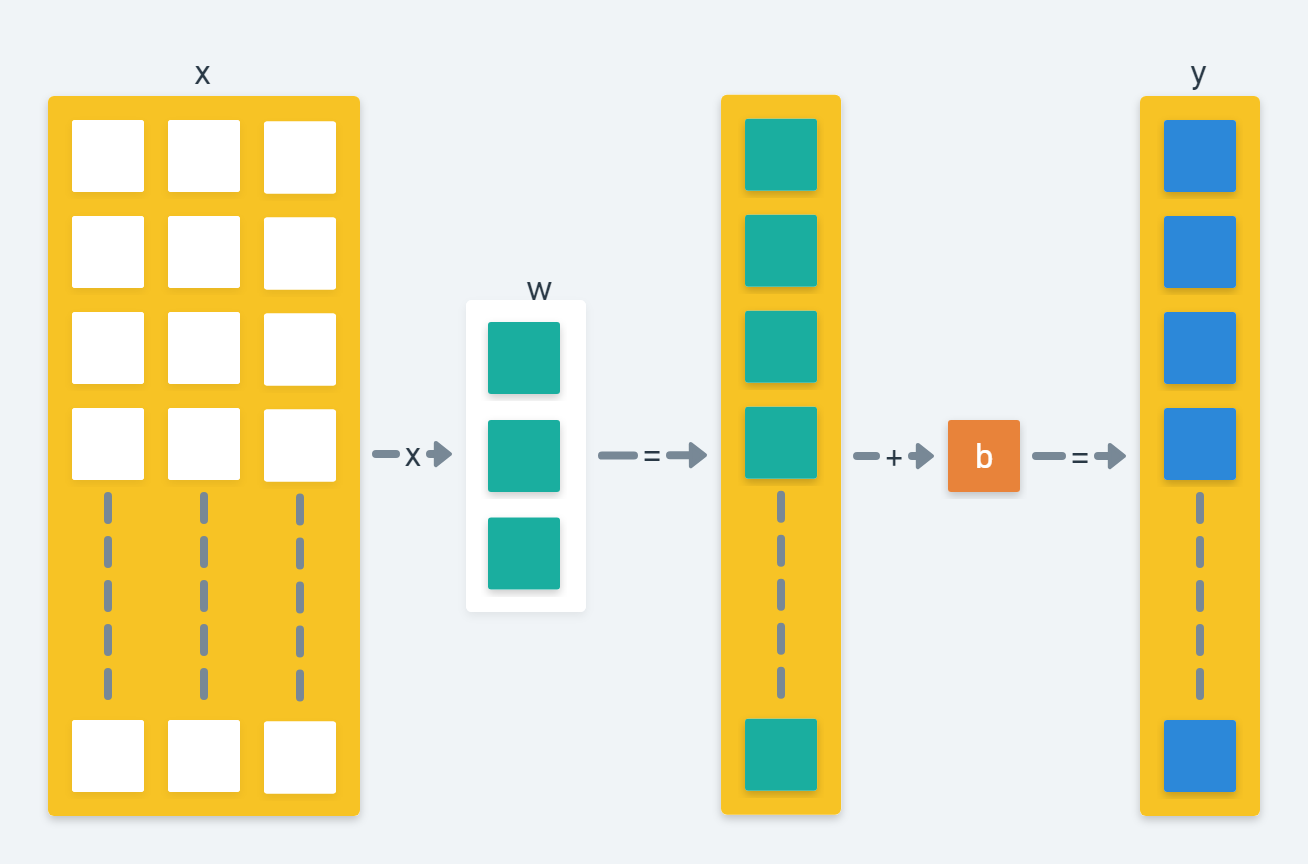
对应的 TensorFlow 代码如下
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,3])
w = tf.Variable([[0,0,0]],dtype=tf.float32,name='weights')
b = tf.Variable(0,dtype=tf.float32,name='bias')
y_pred = tf.matmul(w,tf.transpose(x)) + b
这里的 w 和 b 是模型的变量,我们的目标就是找到合适的 w 和 b 以使结果值 y_pred 和目标值差异最小化。
Loss Function
损失函数是指在计算过程某一步的结果与目标结果的差异,最常用的损失函数有均方误差 (Mean squared error)。 这里我们就使用 TensorFlow 的均方误差函数来计算损失差异。
y_true 是我们要达到的某个目标值,后面我们会创造这个样例数据
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_true-y_pred))
Optimizer
有了函数模型计算,有了比较结果差异的损失函数,我们还需要给 TensorFlow 指定如何改变模型的变量(如 w 和 b)以找到最优解即结果差异最小化。这就是优化器 (Optimizer) 的工作,我们这里使用常用的一种梯度下降法(Gradient descent)优化器
tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer 。
learning_rate = 0.5
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
Sampling methods
为了训练我们的 TensorFlow 模型,要创建一些样例数据和目标值给他,结合之前的模型函数,这里再为其叠加一些高斯噪音(要不然 TensorFlow 很快就能找到完全最优的目标值)
\[y_i = f(x_i) + \varepsilon_i\]下面使用 numpy 库创造一些 2000 个的样例数据,w 设为 [0.3,0.5,0.1] b 设为 -0.2,用随机函数生成噪音数据
import numpy as np
# === Create data and simulate results =====
x_data = np.random.randn(2000,3)
w_real = [0.3,0.5,0.1]
b_real = -0.2
noise = np.random.randn(1,2000)*0.1
y_data = np.matmul(w_real,x_data.T) + b_real + noise
Train
最后完整流程为
模型函数 + 损失函数 + 优化器 => 最优值
完整代码如下
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# === Create data and simulate results =====
x_data = np.random.randn(2000,3)
w_real = [0.3,0.5,0.1]
b_real = -0.2
noise = np.random.randn(1,2000)*0.1
y_data = np.matmul(w_real,x_data.T) + b_real + noise
NUM_STEPS = 10
g = tf.Graph()
wb_ = []
with g.as_default():
#x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,3])
x = tf.Variable(tf.ones(shape=[1,3]), name="x")
#y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=None)
y_true = tf.Variable(tf.ones([1]), name="y")
with tf.name_scope('inference') as scope:
w = tf.Variable([[0,0,0]],dtype=tf.float32,name='weights')
b = tf.Variable(0,dtype=tf.float32,name='bias')
y_pred = tf.matmul(w,tf.transpose(x)) + b
with tf.name_scope('loss') as scope:
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_true-y_pred))
with tf.name_scope('train') as scope:
learning_rate = 0.5
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# Before starting, initialize the variables. We will 'run' this first.
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for step in range(NUM_STEPS):
sess.run(train,{x: x_data, y_true: y_data})
if (step % 5 == 0):
print(step, sess.run([w,b]))
wb_.append(sess.run([w,b]))
print(10, sess.run([w,b]))
TensorFlow 2.2.0
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras as ks
from tensorflow.estimator import LinearRegressor
Comments