- Persistency and Data Model
- Step 1. Defining the Business Object
- Step 2. 用 Annotation 生成 BOPF
- Step 3. Implementing a Service-Specific Consumption View
- Step 4. Create SAP Fiori App for Business Object
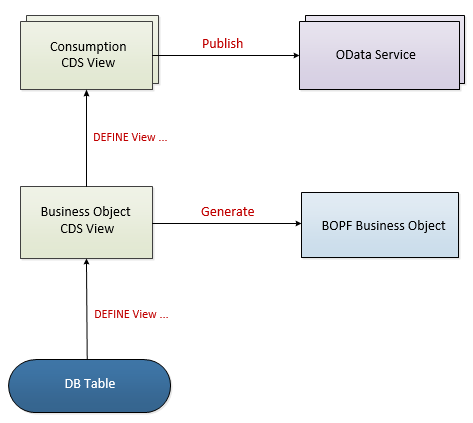
In this chapter, we will develop - step by step - quite a simple sales order application, starting with the creation of a basic persistence model. We will then define a normalized data model, followed by the provision of a service-specific consumption view. After this, we are going to build a Fiori UI using Smart Templates as Fiori building blocks and test the resulting app within the SAP Fiori Launchpad. In our final step, we will extend the application’s business logic with actions that are implemented with the help of BOPF API.
Persistency and Data Model
As with any other business application, a set of database tables and other Dictionary objects defines the persistence model of a transaction application. As a data source for a business object to be generated, a database table needs to be provided for each so-called business object CDS view (also referred to as business object views). Generally, business object views are normalized CDS views that define the hierarchy of entities by using associations and @ObjectModel annotations. A business object view is defined on top of the underlying database table or the CDS view and exposes all elements that are defined in the SELECT list, including the key elements that correspond to the primary keys of the underlying database table. In the transactional scenario of the programming model for SAP Fiori, the business object view is required for business object generation on the basis of the BOPF framework.
A consumption CDS view (also referred to as consumption view) allows the consumption of a business object view in a different manner by different OData services. Each service-specific view is defined on top of a business object view and exposes its fields. A consumption view enhances the data model with metadata, additional associations, or even with transient fields that fit to a given consumption use case. In particular, the consumption views are used to enhance the data model with UI-specific annotations for later consumption in Fiori UIs.
Step 1. Defining the Business Object
We will first create a suitable database table for Sales Order header data using ABAP Dictionary tools and then use this as a data source for a new data model.
Since SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP 7.52 SP00, you can create and work with database tables in ABAP Development Tools (ADT) using the source-based editor.
使用 ADT 工具创建 database table ZTAB_SO
在代码编辑器里填入以下内容
@EndUserText.label : 'My Demo: Sales Order Table'
@AbapCatalog.enhancementCategory : #EXTENSIBLE_CHARACTER_NUMERIC
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #L
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #ALLOWED
define table ztab_so {
@AbapCatalog.foreignKey.screenCheck : true
key client : mandt not null
with foreign key [0..*,1] t000
where mandt = ztab_so.client;
key salesorder : snwd_so_id not null;
businesspartner : snwd_partner_id;
currencycode : snwd_curr_code;
@Semantics.amount.currencyCode : 'ztab_so.currencycode'
grossamount : snwd_ttl_gross_amount;
@Semantics.amount.currencyCode : 'ztab_so.currencycode'
netamount : snwd_ttl_net_amount;
billingstatus : snwd_so_cf_status_code;
overallstatus : snwd_so_oa_status_code;
include /bobf/s_lib_admin_data;
}
保存并激活此表, 然后在 SE11 中便可以看到此表.
Step 2. 用 Annotation 生成 BOPF
This step demonstrates how you can implement a Business Object view to provide a normalized data model for a simple Sales Order application.
传统的方式创建 BOPF 是直接创建 BOPF 对象然后自动生成相应的物理表. 这里 CDS 的方式有所不同, 先是创建物理表, 然后再在物理表之上创建相应 Business Object view , 然后为此 view 添加 annotations 来生成对应的 BOPF business object.
The annotations (required) for each root entity are:
@ObjectModel.modelCategory: #BUSINESS_OBJECT: Serves for semantic categorization only (the CDS view represents a business object) in the context of the Virtual Data Model (VDM). The model category is an optional annotation and has no runtime effect. We recommend adding this annotation to views representing the root node of a business object.@ObjectModel.compositionRoot: true: Defines the root of the compositional hierarchy for the business object to be created@ObjectModel.transactionalProcessingEnabled: true: Enables transactional runtime support
the following annotations are required for all editable entities (including the root entity):
@ObjectModel.writeActivePersistence: '<database_table/view>: Specifies the database table or the database view for storing BO data changes that result from transactional behavior@ObjectModel.createEnabled: true: Allows you to create new business object instances@ObjectModel.deleteEnabled: true: Allows you to delete business object instances@ObjectModel.updateEnabled: true: Allows you to update existing business object instances
Step 2.1 Adding Business Object Semantics to Data Model
在 ADT 中创建 CDS View ZDEMO_I_SalesOrder_TX (注意:区分大小写)
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZDEMO_I_SO'
@AbapCatalog.compiler.compareFilter: true
@AbapCatalog.preserveKey: true
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Sales Order for transactional app'
@ObjectModel.semanticKey: 'SalesOrder'
@ObjectModel.modelCategory: #BUSINESS_OBJECT
@ObjectModel.compositionRoot: true
@ObjectModel.transactionalProcessingEnabled: true
@ObjectModel.writeActivePersistence: 'ZTAB_SO'
@ObjectModel.createEnabled: true
@ObjectModel.deleteEnabled: true
@ObjectModel.updateEnabled: true
define view ZDEMO_I_SalesOrder_TX
as select from ztab_so as SalesOrder
association [0..1] to SEPM_I_BusinessPartner as _BusinessPartner on $projection.BusinessPartner = _BusinessPartner.BusinessPartner
association [0..1] to SEPM_I_Currency as _Currency on $projection.CurrencyCode = _Currency.Currency
association [0..1] to SEPM_I_SalesOrderBillingStatus as _BillingStatus on $projection.BillingStatus = _BillingStatus.SalesOrderBillingStatus
association [0..1] to Sepm_I_SalesOrdOverallStatus as _OverallStatus on $projection.OverallStatus = _OverallStatus.SalesOrderOverallStatus
{
key SalesOrder.salesorder as SalesOrder,
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_BusinessPartner'
SalesOrder.businesspartner as BusinessPartner,
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Currency'
@Semantics.currencyCode: true
SalesOrder.currencycode as CurrencyCode,
@Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode'
SalesOrder.grossamount as GrossAmount,
@Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode'
SalesOrder.netamount as NetAmount,
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_BillingStatus'
SalesOrder.billingstatus as BillingStatus,
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_OverallStatus'
SalesOrder.overallstatus as OverallStatus,
/* Associations */
_BusinessPartner,
_Currency,
_BillingStatus,
_OverallStatus
}
SEPMRA_I_SalesOrderTP这个代码样例比较全.
Step 2.2 Generated Business Object
After ensuring that the syntax of the CDS view is complete and correct, activate the data definition (as the corresponding development object).
CDS View + @ObjectModel 激活后 BOPF runtime 便会生成对应的 business object ZDEMO_I_SALESORDER_TX (注意: 字符大写) 在同一个开发包里. 也可以在 CDS View Editor 左边框看到提示生成成功信息.
在 ADT 打开 BO editor 或者在 SAP GUI 中打开(事务码: BOBX) , 可以看到此 business object 的 Constants Interface 等信息, 还可以链接到详情界面.
Constants Interface is an ABAP interface that is dedicated to a specific business object. The interface includes constants for each business object’s entity like nodes, attributes, actions and so on. We will be using it later on when we add an action to the business object generated.
Step 2.3 Testing CRUD Operations in the BOPF Test Shell
对于生成的 business object 还可以在 ADT BOPF test environment 中测试增删改查功能. 在 ADT 中打开 BOPF test environment: Project Explorer tree -> BOPF Business Objects -> business object -> Run As Test Environment
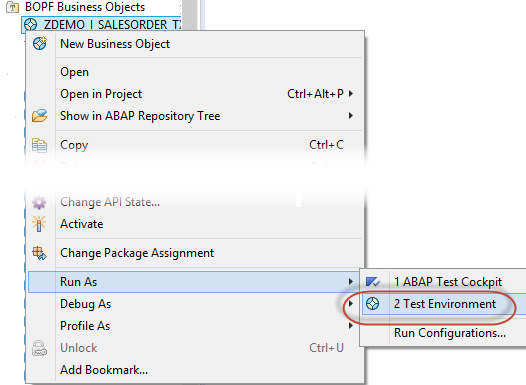
或者在 SAP GUI 中运行事务码 BOBT.
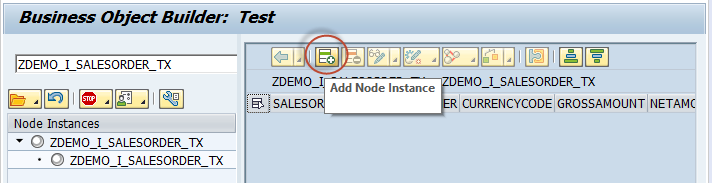
添加行记录:
保存所有记录:
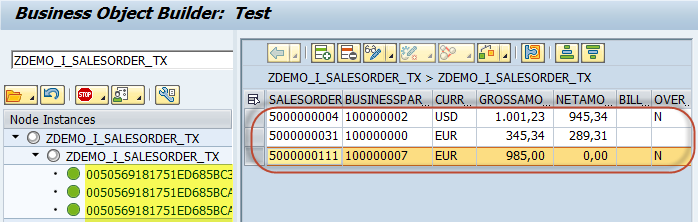
然后就可以在 CDS View 的 data preview 界面查到这些数据了.
Step 3. Implementing a Service-Specific Consumption View
上面步骤我们已经创建了 BO View, 同时实现了增删改查的基本功能. 现在再在其上实现一个用于消费层的消费视图 consumption view. 注解 ObjectModel 可以用在 consumption view 上标明事务相关面.
The annotations (required) for each root entity are:
@ObjectModel.transactionalProcessingDelegated: true: Indicates that transactional access to the consumption view is delegated to the transactional runtime of the underlying view (which is annotated with@ObjectModel.transactionalProcessingEnabled: true).
the following annotations are required for all editable entities (including the root entity):
@ObjectModel.createEnabled: true: Allows the end user to create new business object instances@ObjectModel.deleteEnabled: true: Allows the end user to delete business object instances@ObjectModel.updateEnabled: true: Allows the end user to update existing business object instances
CDS rule: Remember to double-maintain the annotations that have the VIEW scope. In CDS views, only the annotations with ELEMENT and ASSIOCIATION scope are inherited from the business object view.
Step 3.1 Implementing the Data Model for Consumption
在上步创建的 BO View ZDEMO_I_SalesOrder_TX 之上再创建一个 Consumption View ZDEMO_C_SalesOrder_TX:
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZDEMO_C_SO'
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Sales Order for transactional app'
@ObjectModel.semanticKey: 'SalesOrder'
@ObjectModel.transactionalProcessingDelegated: true
@ObjectModel.createEnabled: true
@ObjectModel.deleteEnabled: true
@ObjectModel.updateEnabled: true
@UI.headerInfo: { typeName: 'Sales Order', typeNamePlural: 'Sales Orders' }
@OData.publish: true
define view ZDEMO_C_SalesOrder_TX
as select from ZDEMO_I_SalesOrder_TX as Document
{
@UI.lineItem.position: 10
@UI.identification.position: 10
key Document.SalesOrder,
@UI.lineItem.position: 20
@UI.identification.position: 20
Document.BusinessPartner,
Document.CurrencyCode,
@UI.lineItem.position: 50
@UI.identification.position: 50
Document.GrossAmount,
@UI.lineItem.position: 60
@UI.identification.position: 60
Document.NetAmount,
@UI.lineItem.position: 30
@UI.selectionField.position: 30
@UI.identification.position: 30
Document.BillingStatus,
@UI.lineItem.position: 40
@UI.selectionField.position: 40
@UI.identification.position: 40
Document.OverallStatus,
/* Exposing value via associations */
@UI.lineItem: { value: '.CompanyName', position: 15 }
Document._BusinessPartner,
Document._Currency,
Document._BillingStatus,
Document._OverallStatus
}
@OData.publish: true: 用来生成相应的 OData Service, 也可以在 SEGW 中用 expose CDS View 的方式发布 OData Service.
@ObjectModel.semanticKey: 'SalesOrder': 指定了事务的语义键字段.
Step 3.2 Activating the Data Definition of Consumption View
激活并测试相应的 OData Service, 略.
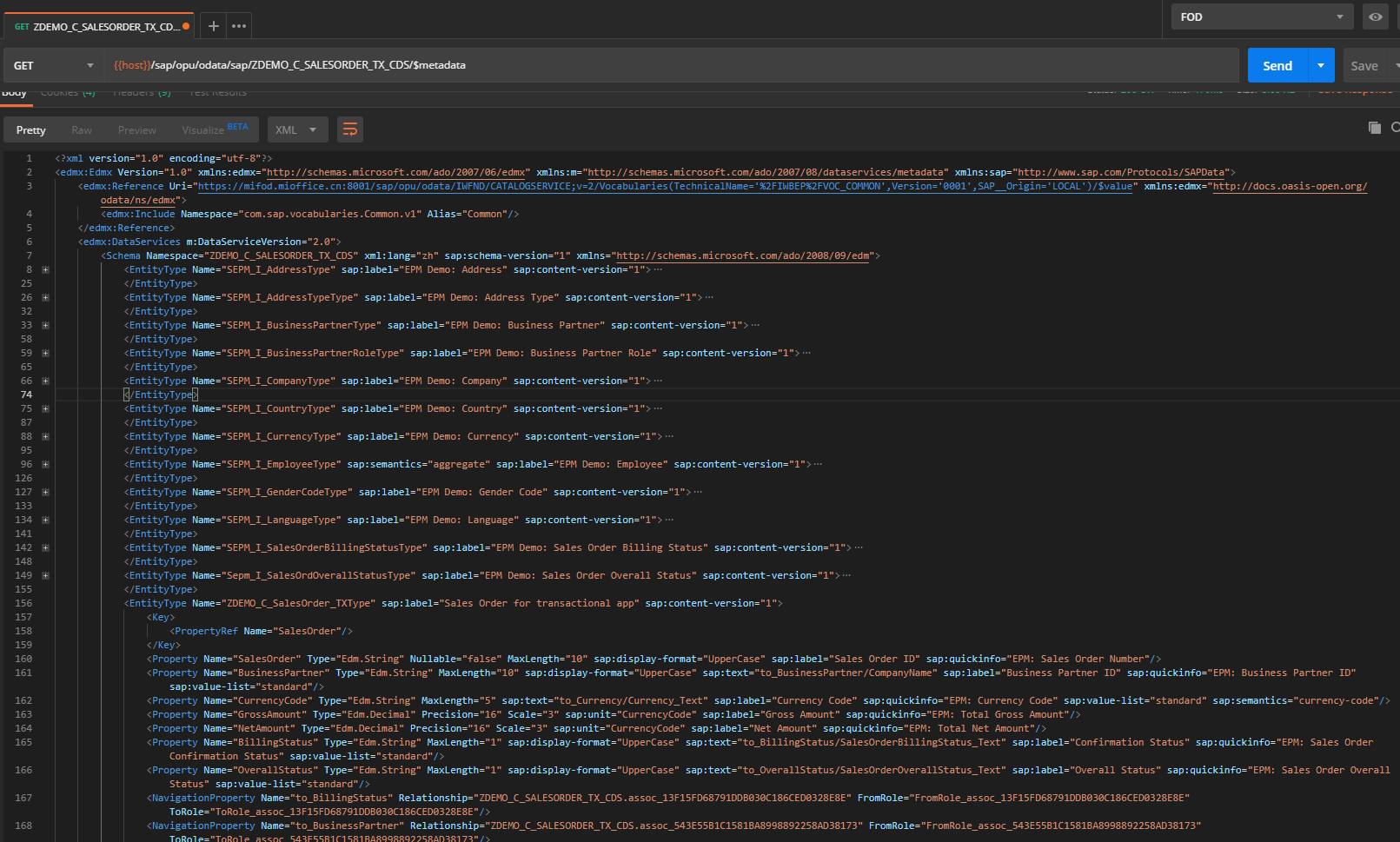
Step 4. Create SAP Fiori App for Business Object
打开 SAP Web IDE, New -> Project from Template -> Select List Reporting Application -> Project Name = Web_Project_for_SOTX -> Title = Web Project for Sales Order TX -> next
在 Service Catalog 里选择上面步骤建的 OData Service -> next -> 勾选两个 Annotation Files -> 选择 ZDEMO_C_SalesOrder_TX 为 OData Collection -> 完成
执行 Run as -> Web Application, 便可以看到如下图 Fiori App 效果, 并且会有之前的测试数据
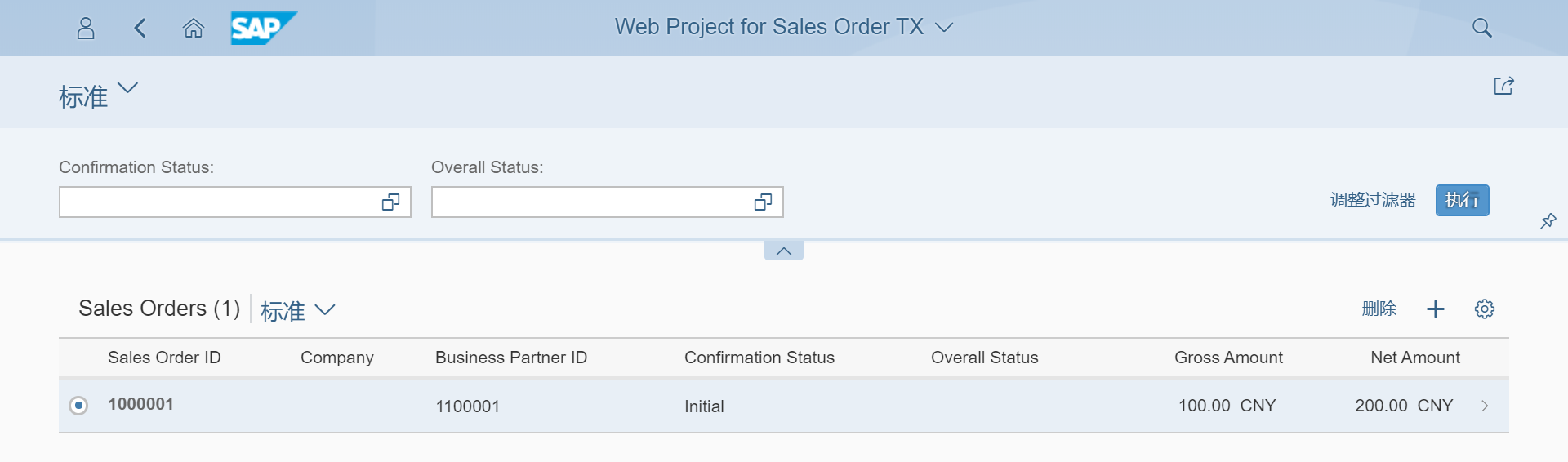
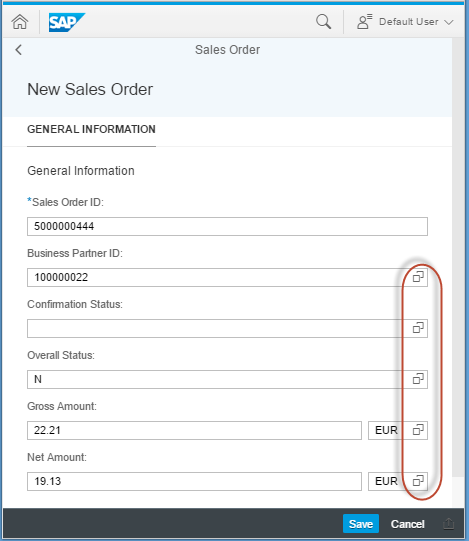
接着就可以使用创建按钮或者删除按钮对数据进行 CRUD 操作了.
Comments