- First Steps
- Docker Fundamentals
- Creating a Simple Web App
- Image Distribution
- Continuous Integration and Testing with Docker
- Deploying Containers
- Logging and Monitoring
- Networking and Service Discovery
First Steps
The Basic Commands
$ docker run -h CONTAINER -i -t debian /bin/bash
Building Images from Dockerfiles
docker build -t test/cowsay-dockerfile .
docker run --rm test/cowsay-dockerfile "Moo world"
Problem: standard_init_linux.go:178: exec user process caused “no such file or directory”
When: make the entrypoint.sh as the ENTRYPOINT
Fixed:dos2unix entrypoint.sh
Docker Fundamentals
The Docker Architecture
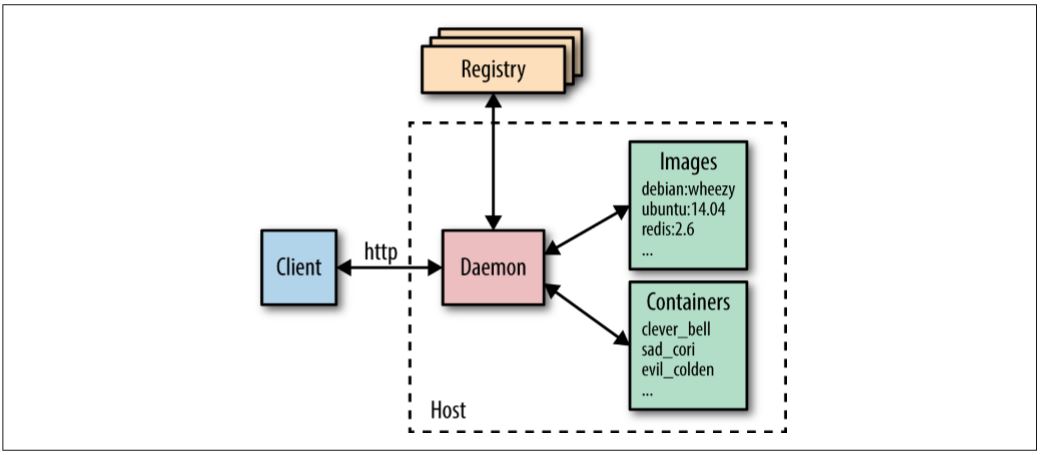
The Docker daemon used an “execution driver” to create containers.
execution driver:
-
runc CLI tool for spawning and running containers according to the OCI specification
-
LXC is a userspace interface for the Linux kernel containment features. Through a powerful API and simple tools, it lets Linux users easily create and manage system or application containers.
Docker storage drivers
Surrounding Technologies
- Swarm
- Compose
- Machine
- Kitematic
- Docker Trusted Registry
- Networking: Weave, Project Calico, Overlay
- Service discovery: Consul, Registrator, SkyDNS, etcd
- Orchestration and cluster management: Kubernetes from Google, Marathon for Mesos, CoreOS’s Fleet, Docker’s Swarm
Docker Hosting
- Amazon cloud
- Google cloud
- Digital Ocean cloud
- Joyent Triton
- Deis
- Flynn
- Paz
How Images Get Built
The Build Context
docker build - < Dockerfile
docker build - < context.tar.gz
docker build -f dockerfiles/Dockerfile.debug
.dockerignore
Image Layers
docker history mongo:latest
Caching
docker build --no-cache
Dockerfile Instructions
Best practices for writing Dockerfiles
Linking Containers
Managing Data with Volumes and Data Containers
docker run -v /dataVOLUME /datadocker run -v /home/tiven/data:/data
Sharing Data
--volumes-from CONTAINER
Data Containers
seed the container with any initial data and ensures permissions are set up correctly.
Delete:
docker rm -v
Common Docker Commands
The Software Lifecycle with Docker
Creating a Simple Web App
FROM python:3.4
RUN groupadd -r uwsgi && useradd -r -g uwsgi uwsgi
RUN pip install Flask==0.10.1 uWSGI==2.0.8 requests==2.5.1 redis==2.10.3
WORKDIR /app
COPY app /app
COPY cmd.sh /
EXPOSE 9090 9191
USER uwsgi
CMD ["/cmd.sh"]
Docker Compose
Image Distribution
Running:
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --restart always --name registry registry:2
Tagging:
docker tag test/jekyll localhost:5000/test/jekyll
Pushing:
docker push localhost:5000/test/jekyll
Continuous Integration and Testing with Docker
Deploying Containers
Provisioning Resources with Docker Machine
docker-machine ls
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox dev
docker-machine regenerate-certs dev if need
docker-machine env dev
docker-machine env dev | Invoke-Expression
docker info
Logging and Monitoring
Part III. Tools and Techniques
Networking and Service Discovery
Ambassadors
docker-machine create -d virtualbox redis-host
docker-machine env redis-host | Invoke-Expression
docker run -d --name real-redis redis:3
docker run -d --name real-redis-ambassador -p 6379:6379 --link real-redis:real-redis amouat/ambassador
docker-machine ip redis-host
Socat is a command line based utility that establishes two bidirectional byte streams and transfers data between them.
sed is a stream editor. A stream editor is used to perform basic text transformations on an input stream (a file, or input from a pipeline). While in some ways similar to an editor which permits scripted edits (such as ed), sed works by making only one pass over the input(s), and is consequently more efficient.
Service Discovery
etcd
etcd is a distributed reliable key-value store for the most critical data of a distributed system.
SkyDNS
SkyDNS is a distributed service for announcement and discovery of services built on top of etcd. It utilizes DNS queries to discover available services. This is done by leveraging SRV records in DNS, with special meaning given to subdomains, priorities and weights.
Comments