R language introduce
R language is is an GNU project which based on S language, it can be treated as an implementation of S language. It is firstly developed by Ross lhaka and Robert Gentleman in the University of Auckland, New Zealand, it mainly used for statistic computing, graphing, and data mining.
Since SAP HANA SP5, it is has been enforced greatly with the integrate of memory computing and the statistic function of R language. This enables you use R as a procedure language, and call the function of R. The data exchange between SAP HANA and R is very efficient, because they all use the column storage style. The communication process between SAP HANA and R is shown below:
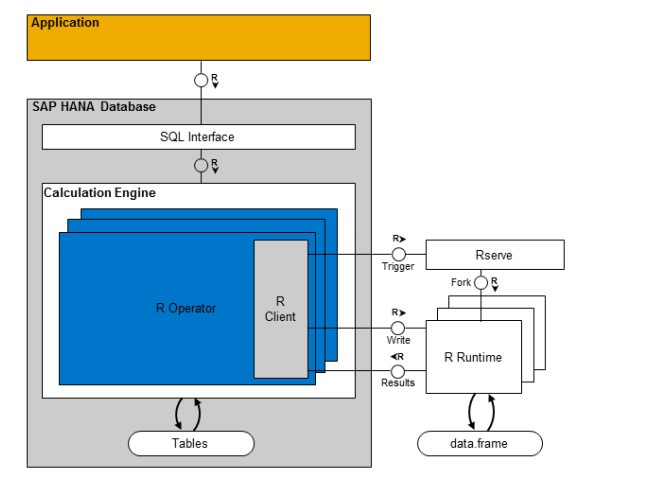
In order to execute R code in SAP HANA, the R code is writen as a procedure with RLANG. It is executed by the external Rserve.For the support of R operator, The calculate engine inside SAP HANA has been extended, for the given input object, after some computing , output with a result table. Differently with the local operator, R operator can be processed by R function, when the calculate engine recognized the R operator, the R client will send a request to the Rserve, and at the same time send the parameters needed by the program, then it will begin to execute, and result data frame will be send back to the calculate engine.
The installation of R
Samples
set schema "<your_schema>";
DROP TABLE "spam"
;
CREATE COLUMN TABLE "spam"("make" DOUBLE, "address" DOUBLE, "all" DOUBLE, "num3d" DOUBLE, "our" DOUBLE, "over" DOUBLE, "remove" DOUBLE, "internet" DOUBLE, "order" DOUBLE, "mail" DOUBLE, "receive" DOUBLE, "will" DOUBLE, "people" DOUBLE, "report" DOUBLE, "addresses" DOUBLE, "free" DOUBLE, "business" DOUBLE, "email" DOUBLE, "you" DOUBLE, "credit" DOUBLE, "your" DOUBLE, "font" DOUBLE, "num000" DOUBLE, "money" DOUBLE, "hp" DOUBLE, "hpl" DOUBLE, "george" DOUBLE, "num650" DOUBLE, "lab" DOUBLE, "labs" DOUBLE, "telnet" DOUBLE, "num857" DOUBLE, "data" DOUBLE, "num415" DOUBLE, "num85" DOUBLE, "technology" DOUBLE, "num1999" DOUBLE, "parts" DOUBLE, "pm" DOUBLE, "direct" DOUBLE, "cs" DOUBLE,"meeting" DOUBLE, "original" DOUBLE, "project" DOUBLE, "re" DOUBLE, "edu" DOUBLE, "table" DOUBLE, "conference" DOUBLE, "charSemicolon" DOUBLE, "charRoundbracket" DOUBLE, "charSquarebracket" DOUBLE, "charExclamation" DOUBLE, "charDollar" DOUBLE, "charHash" DOUBLE, "capitalAve" DOUBLE, "capitalLong" DOUBLE, "capitalTotal" DOUBLE, "type" VARCHAR(5000), "group" INTEGER)
;
DROP PROCEDURE LOAD_SPAMDATA
;
CREATE PROCEDURE LOAD_SPAMDATA(OUT spam "spam") LANGUAGE RLANG AS
BEGIN
##--if the kernlab package is missing see Requirements
library(kernlab)
data(spam)
ind <- sample(1:dim(spam)[1], 2500)
group <- as.integer(c(1:dim(spam)[1]) %in% ind) spam <- cbind(spam, group)
END
;
DROP TABLE "spamTraining"
;
DROP TABLE "spamEval"
;
CREATE COLUMN TABLE "spamTraining" like "spam"
;
CREATE COLUMN TABLE "spamEval" like "spam"
;
DROP PROCEDURE DIVIDE_SPAMDATA
;
CREATE PROCEDURE DIVIDE_SPAMDATA() AS
BEGIN CALL LOAD_SPAMDATA(spam)
;
Insert
into "spamTraining" select
*
from :spam
where "group"=1
;
Insert
into "spamEval" select
*
from :spam
where "group"=0
;
END
;
CALL DIVIDE_SPAMDATA()
;
Alter Table "spamTraining" DROP ("group")
;
Alter Table "spamEval" DROP ("group")
;
Comments