Cloud Foundry components include a self-service application execution engine, an automation engine for application deployment and lifecycle management, and a scriptable command line interface (CLI), as well as integration with development tools to ease deployment processes. Cloud Foundry has an open architecture that includes a buildpack mechanism for adding frameworks, an application services interface, and a cloud provider interface.
Refer to the descriptions below for more information about Cloud Foundry components. Some descriptions include links to more detailed documentation.
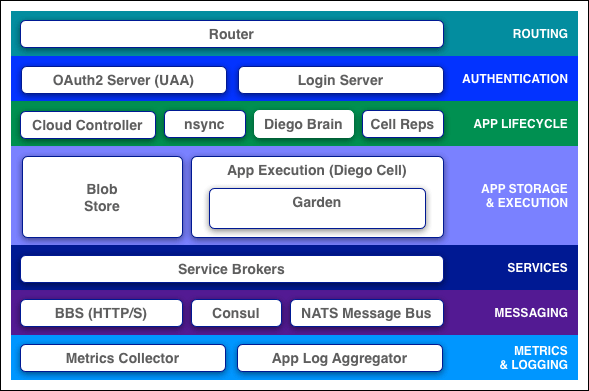
Concepts
Router
The router routes incoming traffic to the appropriate component, either a Cloud Controller component or a hosted application running on a Diego Cell.
The router periodically queries the Diego Bulletin Board System (BBS) to determine which cells and containers each application currently runs on. Using this information, the router recomputes new routing tables based on the IP addresses of each cell virtual machine (VM) and the host-side port numbers for the cell’s containers.
HTTP Routing
Session Affinity
The CloudFoundry Gorouter supports session affinity, or sticky sessions, for incoming HTTP requests to compatible apps.
With sticky sessions, when multiple instances of an app are running on CF, requests from a particular client always reach the same app instance. This allows apps to store session data specific to a user session.
Try
Nodejs
Create a Node.js project using npm init or clone source code of the project from Github git clone https://github.com/anypossiblew/try-cloud-foundry.git
Add a Javascript file for router:
'use strict';
const express = require('express');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const cfenv = require('cfenv');
// create express instance
let oApp = express();
// Cloud Foundry environment variables
let oAppEnv = cfenv.getAppEnv();
/** bodyParser.urlencoded(options)
* Parses the text as URL encoded data (which is how browsers tend to send form data from regular forms set to POST)
* and exposes the resulting object (containing the keys and values) on req.body
*/
oApp.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: true
}));
/**bodyParser.json(options)
* Parses the text as JSON and exposes the resulting object on req.body.
*/
oApp.use(bodyParser.json());
var current_date = (new Date()).valueOf().toString();
var random = Math.random().toString();
var jsessionid = crypto.createHash('sha1').update(current_date + random).digest('hex');
oApp.get('/api/router', function(request, response){
console.log(request.headers);
response.cookie('JSESSIONID', jsessionid, { maxAge: 9000000, httpOnly: true });
response.json({info:"ok"});
});
// express app listener
oApp.listen(oAppEnv.port, function(){
console.log('Server listening at ' + oAppEnv.url);
});
Create the Cloud Foundry manifest (you need change the application name attribute or use attribute random-route: true):
---
applications:
- name: <try-cloud-foundry>
buildpack: nodejs_buildpack
command: node index.js
memory: 128M
disk_quota: 128M
Deploy Application
Deploy the application using cf push -c "node router.js" then you will get the information by executing the command cf app <app-name>
\try-cloud-foundry>cf app try-cloud-foundry
Showing health and status for app try-cloud-foundry in org <tiven.wang> / space development as <email@gmail.com>...
OK
requested state: started
instances: 1/1
usage: 128M x 1 instances
urls: try-cloud-foundry.cfapps.io
last uploaded: Thu Feb 23 09:56:29 UTC 2017
stack: cflinuxfs2
buildpack: nodejs_buildpack
state since cpu memory disk details
#0 running 2017-02-24 05:37:01 AM 0.2% 23.1M of 128M 35.8M of 128M
In order to test the cloud foundry router for multiple instances, you need to scale the application using cf scale <app-name> -i 2 or set attribute instances: 2 in application’s manifest file.
Retry the command cf app <app-name>, you will see:
\try-cloud-foundry>cf app try-cloud-foundry
Showing health and status for app try-cloud-foundry in org <tiven.wang> / space development as <email@gmail.com>...
OK
requested state: started
instances: 2/2
usage: 128M x 2 instances
urls: try-cloud-foundry.cfapps.io
last uploaded: Thu Feb 23 09:56:29 UTC 2017
stack: cflinuxfs2
buildpack: nodejs_buildpack
state since cpu memory disk details
#0 running 2017-02-24 05:37:01 AM 0.0% 23.4M of 128M 35.8M of 128M
#1 running 2017-02-24 11:09:45 AM 0.2% 23.6M of 128M 35.8M of 128M
Refer more tips for Node.js applications on CF platform
Test
Open the url of your application: https://try-cloud-foundry.cfapps.io/api/router in browser, you can get the response as
{
info: "ok"
}
Open the developer tools of browser for the page:
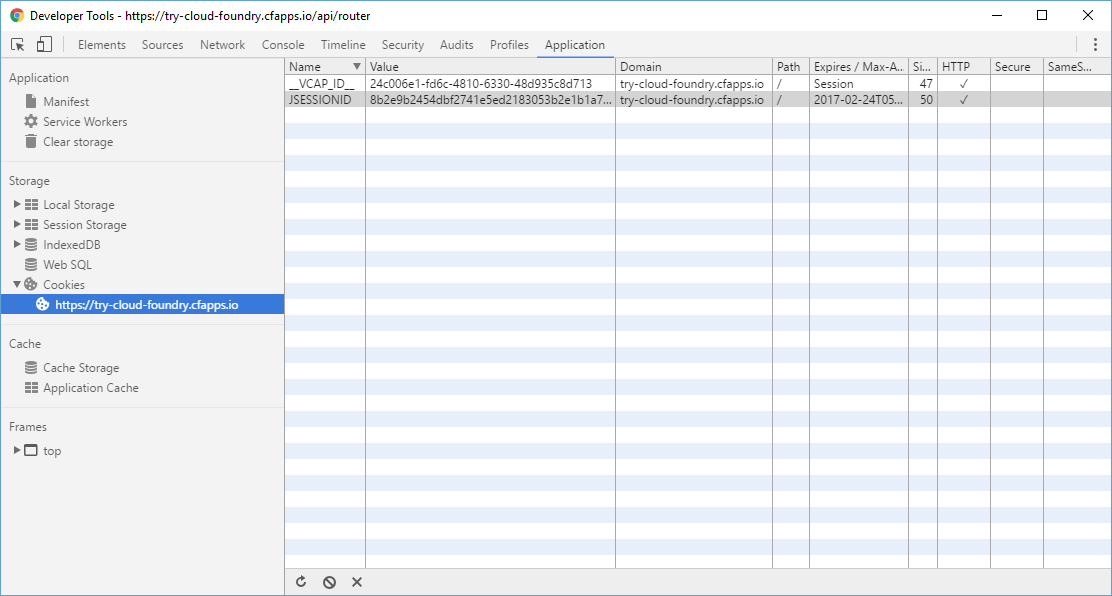
You can see the two attributes in the cookies of the page. Refresh the page, the value will not be changed. But you can remove all of the two attributes, the you might get a different value. Eventually there are only two different values, one belongs to each instances of the application.
Comments